About Food Waste Reduction
Food waste is a critical issue that has significant implications for climate change.
It is estimated that one-third of all food produced in the world is lost or wasted, which amounts to 1.3 billion tons per year.
When food is wasted, not only are resources such as water, land, and energy used to produce the food also wasted, but the greenhouse gases produced in the production of the food are also released unnecessarily.
Addressing food waste has been identified as a significant climate solution, with Project Drawdown ranking it as the 4th most effective solution (1.5C scenario and top scenario of impact 2C scenario). The report estimates that reducing food waste by 50% by 2050 could avoid 26.2 gigatons of carbon dioxide equivalent emissions, making it a critical solution in the fight against climate change.
Reducing food waste involves actions at all levels, from individuals reducing their food waste at home to food companies and governments implementing policies and practices to prevent waste throughout the food supply chain. These actions can include improving storage and transportation practices, changing expiration labeling, and redistributing food to those in need.
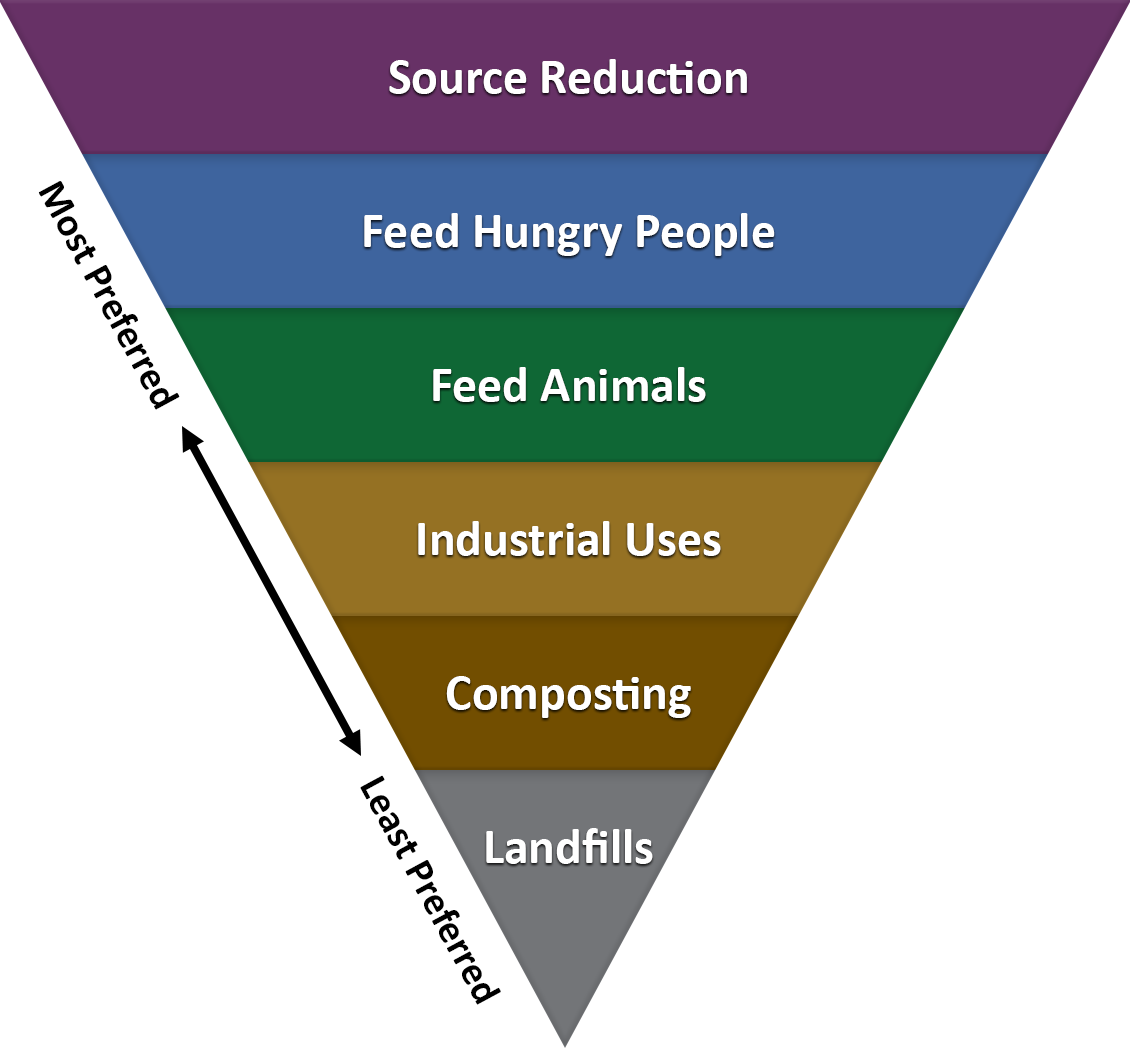
The “Food Recovery Hierarchy” was developed by the U.S. EPA and has been adopted and adapted by many countries around the world.
It is based on the 3 steps needed to avoid sending Food Waste to landfill: Prevention, Rescue and Recycling/Repurposing
ReFed have done an extensive analysis on solving Food Waste in the USA and have identified 7 key levers consistent with the Food Waste Hierarchy. Find out more at Refed >>

Credit: Refed, www.refed.org
One example of an inspiring solution story. let’s gather lots more!
Community Composting Hubs
(As featured on the War On Waste episode Aug 3 2023)